Chapter: Rain, Thunder, and Lightning
CBSE Class 8 Science Notes
➥ Static Electricity: The chemical charge generated by rubbing is called static electricity because these charges do not transmit.
➥ There are two types of charges—positive charge and negative charge.
➥ When we rub two objects, made of different substances, together the charge they acquire are opposite to each other.
➥ Electric Current: When charges move, they constitute an electric current.
➥ Electric charges are of two types:
- Positive Charge: When the charge of an object is due to the loss of electrons.
- Negative Charge: When the charge of an object is due to the excess of electrons.
➥ Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract each other.
➥ An Electroscope is a device used to detect whether an object is carrying an electric charge or not.
➥ Voltage: The potential difference between two points in an electric field is called voltage.
➥ Atmospheric electricity refers to the electric charge that exists naturally in the Earth's atmosphere. Lightning is a large-scale example of atmospheric electricity.
➥ Lightning is the process of electric discharge between clouds and the Earth, or between different clouds.
➥ When negative charges from the clouds meet positive charges on the ground, a huge amount of energy is produced as bright light and sound, which we observe as lightning.
➥ Thunderstorm: A storm accompanied by thunder and lightning, often resulting from moisture and warm air rising into the atmosphere.
➥ Thunder: The loud noise that accompanies lightning during a thunderstorm.
➥ While lightning can be dangerous, it plays a role in the natural environment by helping fix nitrogen in the soil, making it available for plants to absorb.
➥ Lightning conductors protect tall buildings by directing the electric discharge safely into the ground, preventing damage.
| Objects that get charged | Material used for rubbing |
|---|---|
| Refill | Polythene, woollen cloth |
| Balloon | Polythene, woollen cloth, dry hair |
| Eraser | Wool |
| Steel spoon | Polythene, woollen cloth |
| Ebonite comb | Dry hair, silk cloth |
| Glass rod | Woollen cloth, silk cloth |
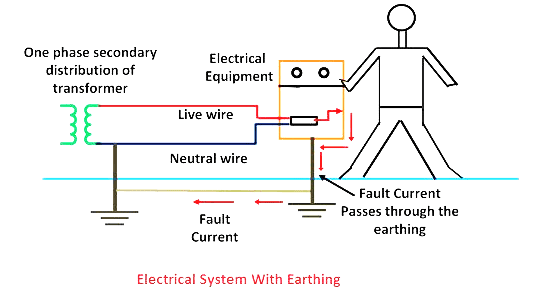
➥ Earthing: The process of transfer of charges from a charged object to the Earth is called earthing.
➥ Earthing is provided in electrical wiring in buildings to protect us from electrical shocks in case of any leakage of electrical current.
➥ Electric charge can be transferred from a charged object to another through a conductor.
➥ The static charge in the clouds is the cause of lightning.
➥ The process of electric discharge between clouds and the Earth or between different clouds causes lightning.
➥ When negative charges from the clouds and positive charges on the ground meet, a huge amount of energy is produced as bright light and sound, which we see as lightning. The process is called electric discharge.
➥ An earthquake is a sudden shaking or trembling of the Earth.
➥ Earthquake is caused by a disturbance deep inside the Earth’s crust.
➥ It is not possible to predict the occurrence of an earthquake.
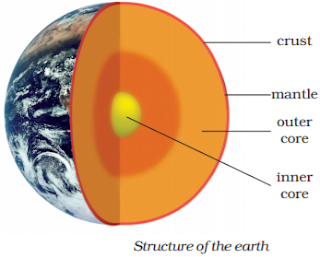
➥ The outermost layer of the earth is not in one piece. It is fragmented. Each fragment is called a plate.
➥ Earthquakes tend to occur at the boundaries of Earth’s plates. These boundaries are known as fault zones.
➥ Crust is the uppermost layer of Earth’s surface (8 km – 32 km).
➥ Destructive energy of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale. The earthquake measuring 7 or more on the Richter scale can cause severe damage to life and property.
➥ The seismic waves are recorded by an instrument in the form of a graph called the seismograph.
➥ Earthquakes may cause tsunamis in oceans, resulting in huge damage in coastal areas.
➥ Tremor: Trembling or shaking of the Earth.
Subscribe to My Channel









No comments:
Post a Comment