📘 Chapter: Database Management System – MS Access 2016
🗃️ 1. Database and its Management
➥ A Database is a collection of related information organized in a way that it can be easily accessed, managed, and updated.
➥A Database Management System (DBMS) is software that helps in creating and managing databases.
➥ MS Access 2016 is a DBMS developed by Microsoft to store, manage, and analyze information quickly and easily.
📂 2. Structure of a Database
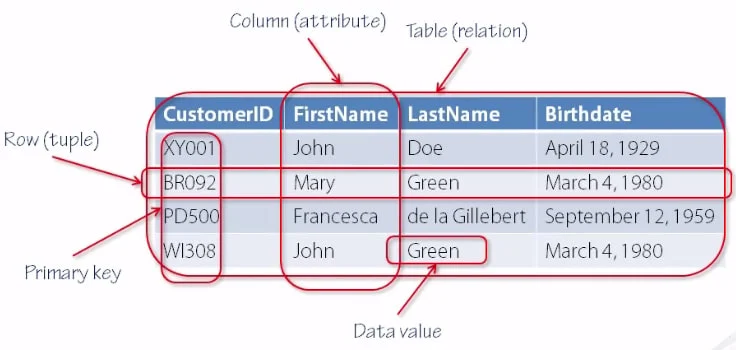
1. Tables – Where data is stored in rows and columns.
2. Queries – Used to search and filter data.
3. Forms – Used to enter and view data in a user-friendly format.
4. Reports – Used to print data in a neat layout.
5. Macros & Modules – Used to automate tasks (advanced use).
🖥️ 3. Starting MS Access 2016
➥ Click on Start Menu.
➥ Search for Access 2016 and click on it.
➥ The MS Access welcome screen will open.
📁 4. Creating a Blank Database
➯ On the MS Access home screen, click on Blank Database.
➯ Type a name for your database in the File Name box.
➯ Click on Create.
➯ A blank table opens in Datasheet View where you can start entering data.
🧩 5. Components of a Database
1. Field – A column in a table (like Name, Age, Address).
2. Record – A row in a table (complete set of data for one person or item).
3. Table – Collection of fields and records.
4. Primary Key – A unique field that identifies each record (like Roll Number).
5. Data Type – Type of data stored (Text, Number, Date/Time, etc.).
📂 6. Opening an Existing Database
➱ Open MS Access.
➱ Click on Open Other Files.
➱ Browse and select your database file.
➱ Click Open.
🔒 7. Closing a Database
➱ Click on File Menu, then select Close.
➱ This closes the database but keeps the MS Access window open.
❌ 8. Closing the Access Window
➱ Click the ‘X’ button at the top-right corner of the window to close MS Access completely.
Video Tutorial
You Learn More
Visit GCF Global Learning PageMS Access 2016 Worksheet
DBMS Evaluation Worksheet
A. Tick (✔) the correct option:
- A DBMS stores data in the form of a table: ✔ a. relational
- Which of the following is not a DBMS software application? ✔ a. Microsoft Word
- The is/are located below the Ribbon on the right side of the window: ✔ b. object tabs
- Which keyboard key combination is used to open an existing database? ✔ a. Ctrl + O
B. Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
- A structured collection of data, stored and accessed electronically very easily, is known as Database.
- A DBMS provides a way to maintain the access control and security of the data.
- The repetition of same data at different places is known as data redundancy.
- A query allows the accessing, retrieving and processing of the data stored in a database.
C. Write 'T' for True and 'F' for False:
- A database cannot be classified on the basis of the link between the data — F
- Every record in a table contains the same number of fields — T
- A query is usually created to obtain a printed copy of the data — F
- The Control buttons are located above the title bar — F
D. Answer the following questions:
- How is a database management system easy to learn?
A DBMS provides a user-friendly interface with graphical tools and wizards that help users easily manage data without deep technical knowledge. - How can you create a blank database in Access 2016?
Open Access → Click on "Blank Database" → Enter a file name → Click "Create". - What is meant by data inconsistency? What are the other ways a DBMS can be helpful?
Data inconsistency occurs when different versions of the same data exist in different places. A DBMS helps by reducing redundancy, ensuring data integrity, providing security, and allowing easy access and manipulation of data. - What are the various objects that are commonly used to maintain a database?
The commonly used database objects are: Tables, Queries, Forms, Reports, Macros, and Modules.
E. Define the following terms:
- Data: Raw facts and figures that have no meaning on their own.
- Redundancy: The unnecessary repetition of data in a database.
- RDBMS: Relational Database Management System – A type of DBMS that stores data in related tables.
- Form: A user-friendly interface used to enter, modify, and view data in a database.
- Ribbon: A toolbar in Access (and other MS Office apps) that contains groups of commands and tools organized under tabs.





No comments:
Post a Comment