
Chapter 6: Introduction to HTML
What is HTML?
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language.
- HTML is the standard markup language for creating web pages.
- HTML describes the structure of a web page.
- HTML consists of a series of elements.
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content.
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc.
A Simple HTML Document:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Example Explained-
- The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines that this document is an HTML5 document.
- The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page.
- The <head> element contains meta information about the HTML page.
- The <title> element specifies a title for the HTML page (which is shown in the browser's title bar or in the page's tab).
- The <body> element defines the document's body, and is a container for all the visible contents, such as headings, paragraphs, images, hyperlinks, tables, lists, etc.
- The <h1> element defines a large heading.
- The <p> element defines a paragraph.
What is an HTML Element?
➥ An HTML element is defined by a start tag, some content, and an end tag: <tagname> Content goes here... </tagname>
for Example-
| Start tag | Element content | End tag |
|---|---|---|
| <h1> | My First Heading | </h1> |
| <p> | My first paragraph. | </p> |
| <br> | none | none |
Web Browsers
➥The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them correctly.
➯A browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document.

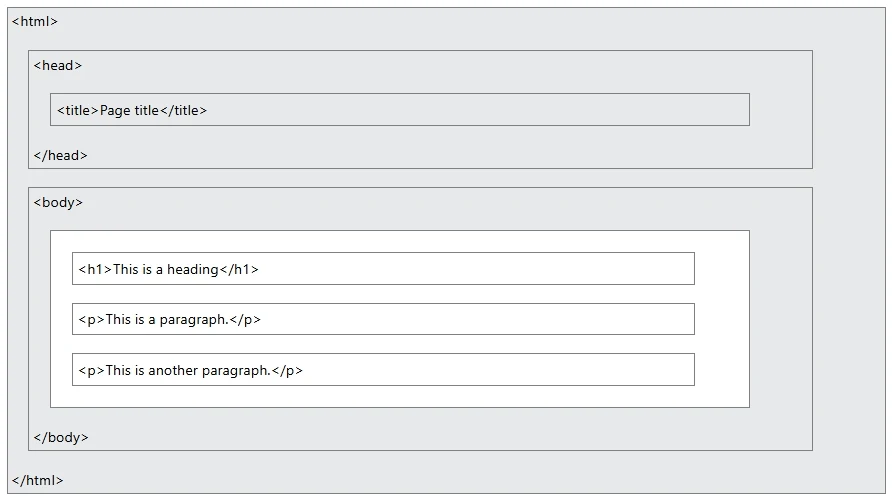
HTML Page Structure
➥ Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
| Year | Version / Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invented WWW |
| 1991 | Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML |
| 1993 | Dave Raggett drafted HTML+ |
| 1995 | HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0 |
| 1997 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 3.2 |
| 1999 | W3C Recommendation: HTML 4.01 |
| 2000 | W3C Recommendation: XHTML 1.0 |
| 2008 | WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft |
| 2012 | WHATWG HTML5 Living Standard |
| 2014 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5 |
| 2016 | W3C Candidate Recommendation: HTML 5.1 |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.1 2nd Edition |
| 2017 | W3C Recommendation: HTML5.2 |
Learn HTML Using Simple Editors
➯ To learn HTML, a simple text editor like Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on Mac is sufficient.
Professional HTML editors are available but are not necessary for beginners.
Simple Step-by-Step
- Open editor: Notepad (Windows) or TextEdit → Preferences → Plain Text (Mac).
- Write this code: (copy below into your editor)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>My First Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World!</h1>
<p>This is my first webpage.</p>
</body>
</html>
- Save the file: File → Save As → name index.html, encoding = UTF-8.
- Open in browser: Double-click the file or Right-click → Open With → Chrome/Firefox/Edge.
- Edit & refresh: Change the file in your editor, save, then refresh the browser to see results.

Some Important tag
HTML Headings
➥ HTML provides six levels of headings, <h1> being the largest, and <h6> the smallest.
<h1>Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Heading 3</h3>
<h4>Heading 4</h4>
<h5>Heading 5</h5>
<h6>Heading 6</h6>Container
➥ Container tags are the tags that contain some data such as text, image, etc. There are several container tags in HTML.
div tag
➥ The div tag or division tag is used to make blocks or divisions in the document.
<div> This is div block </div>span tag
➥ The span is a container for inline content.
<span> This is span block </span>p tag
➥ The p tag is used to create a paragraph in HTML.
<p> This is a paragraph </p>pre tag
➥ The pre tag represents pre-formatted text.
<pre> Hello World </pre>code tag
➥ The code tag is used to represent source codes in HTML.
<code>import python</code>Text Formatting
➥ Text formatting tags are used to format text or data in HTML documents. You can make text bold, italic, and emphasize it to improve appearance and clarity.
- <b> tag: I'm bold text
- <strong> tag: I'm important text
- <i> tag: I'm italic text
- <em> tag: Emphasized text
- <sub> tag: Subscript
- <sup> tag: Superscript
Lists
➥ Lists can be numerical, alphabetic, bullet, or other symbols. You can specify list type and items for a clean document.
Ordered List (<ol>)
<ol>
<li>Data 1</li>
<li>Data 2</li>
<li>Data 3</li>
</ol>
Result:-
- Data 1
- Data 2
- Data 3
Unordered List (<ul>)
<ul>
<li>Your Data 1</li>
<li>Your Data 2</li>
</ul>
Result:-
- Your Data
- Your Data
Media
➥ Media includes audio, images, and videos in digital form.
audio tag
➯To play an audio file in HTML, use the <audio> element:
<audio controls>
<source src="demo.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Your browser does not support the audio element.
</audio>
<audio> Autoplay
➯ To start an audio file automatically, use the autoplay attribute:
<audio controls autoplay>
<source src="horse.ogg" type="audio/ogg">
<source src="horse.mp3" type="audio/mpeg">
Your browser does not support the audio element.
</audio>
Try it Yourself »
<img> Tag
➥ The HTML <img> tag is used to embed an image in a web page. The alt attribute should describe the image.
<img src="source_of_image.jpg" alt="Description of image"> <img src="wrongname.gif" alt="Flowers in Chania">
Video Tag
➥ The HTML <video> element is used to show a video on a web page.
<video width="480" height="320" controls>
<source src="demo_move.mp4" type="video/mp4">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
Autoplay Muted Video
➯Many browsers block autoplay unless the video is muted. Add the muted attribute along with autoplay in <video> to ensure it plays automatically.
<video width="320" height="240" autoplay muted>
<source src="movie.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="movie.ogg" type="video/ogg">
Your browser does not support the video tag.
</video>
Table
➥ A table represents data with rows and columns.
Table Structure
<table>
<caption>Demo Table</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Column1</th>
<th colspan="2">Column2</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Data1</td>
<td>Data2</td>
<td>Data2</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Data1</td>
<td>Data2</td>
<td>Data2</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td>Data</td>
<td>Data</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
Try it Yourself »
Links
➥ Links are clickable texts that redirect users to other pages.
<a href="https://www.codewithharry.com/">Visit CodeWithHarry.com!</a>
Form
➥ Forms collect user input and send data to a server.
<form action="/action.php" method="post">
<textarea cols="20" name="comments" rows="5">Comment</textarea><br />
<label><input name="terms" type="checkbox" value="tandc" />Accept terms</label> <br />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
Form Elements
- Text Input: <input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Enter Username">
- Password Input: <input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Enter Password">
- Checkbox: <input type="checkbox" name="agree" value="yes"> I agree
- Radio Button:
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male"> Male
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female"> Female - Submit Button: <input type="submit" value="Submit">
- Button: <button type="button">Click Me</button>
- Select (Dropdown) List:
<select name="country"> <option value="usa">United States</option> <option value="canada">Canada</option> </select> - Textarea: <textarea name="comments" rows="4" cols="50">Enter comments here</textarea>
- File Input: <input type="file" name="fileupload">
- Range Input: <input type="range" name="volume" min="0" max="100">
- Number Input: <input type="number" name="quantity" min="1" max="10">
- Email Input: <input type="email" name="email" placeholder="Enter Email">
- Search Input: <input type="search" name="query" placeholder="Search">
- URL Input: <input type="url" name="website" placeholder="Enter URL">
- Date Input: <input type="date" name="birthdate">
Characters & Symbols
➥ Some symbols are not directly available on keyboard but can be shown using HTML entities.
- Copyright Symbol (©): ©
- Less than (<): <
- Greater than (>): >
- Ampersand (&): &
- Dollar ($): $
Semantic Elements
➥ Semantic elements clearly convey their meaning through their names.
<section>This is a section</section>
<article>Enter your data here</article>
<aside>Your data</aside>Meta Tags
➥ Meta tags define metadata about the document.
<meta name="description" content="This is a description of the page">
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, CSS, JavaScript">
<meta name="author" content="Author Name">
CSS Integration
➥ You can style HTML documents using internal or external CSS.
Internal CSS
<style>
body { background-color: lightblue; }
</style>
External CSS
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
Accessibility
Make your webpage accessible using alternative text and labels.
<img src="image.jpg" alt="Description of Image">
<label for="name">Name:</label> <input type="text" id="name" name="name">
Responsive Design
➥ Design webpages that adapt to screen sizes using meta viewport and media queries.
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<style>
@media (max-width: 600px) {
body { font-size: 18px; }
}
</style>
JavaScript Integration
➥ Embed JavaScript directly or link to external files for added functionality.
Inline Script
<script>
alert('Hello, World!');
</script>
External Script
<script src="script.js"></script>
Comments
➥ Use comments to leave notes inside code. They are ignored by browsers.
<!-- This is a comment -->

No comments:
Post a Comment