Chapter: LIGHT
Class-8th Chapter - Light By Pratap Sanjay Sir
Light:
- It is a form of energy that enables us to see.
- Light always travels in a straight line.
- Light has the maximum speed in this world. Its value is 3x108 m/s.
Sources of Light
- Luminous Sources: Objects that generate their own light.
Examples: Sun (natural source), stars, fire, electric bulbs. - Non-Luminous Sources: Objects that do not emit light but are visible because they reflect light from luminous sources.
Examples: Moon, planets, everyday objects like books, tables, and walls.
Transparent, Translucent, and Opaque Objects
- Transparent: Materials that allow all light to pass through (e.g., clear glass).
- Translucent: Materials that allow some light to pass through (e.g., frosted glass).
- Opaque: Materials that do not allow light to pass through (e.g., wood).
Reflection
➡ Coming back of light rays to the same medium when they fall on a surface.
Laws of Reflection
- Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection (i = r).
- Incident ray, normal at the point of incidence, and reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Regular and Irregular Reflection
- Regular Reflection: Occurs when parallel rays of light hit a smooth surface and reflect in a single direction.
Examples: Reflection from a mirror, calm water surface. - Irregular Reflection: Occurs when parallel rays of light hit a rough surface and scatter in different directions.
Examples: Reflection from rough walls, uneven road surfaces.
Mirror
A smooth, polished surface that reflects light to form images.
Lateral Inversion in a Plane Mirror
➡ The phenomenon where the left side of an object appears as the right side in its image, and vice versa, when viewed in a plane mirror.
Example: The word "AMBULANCE" is often written in reverse on the front of an ambulance so that drivers can read it correctly in their rear view mirrors.
Multiple Reflection by Plane Mirrors
- Occurs when light is reflected multiple times between two or more plane mirrors.
- Two mirrors placed parallel to each other create an infinite series of reflections.
Applications of Multiple Reflection
- Periscope: Uses two plane mirrors placed at 45° angles to allow viewing over obstacles.
- Kaleidoscope: Uses multiple mirrors to create symmetrical patterns through repeated reflection.
- Barber’s Shop Mirrors: Two mirrors facing each other allow the customer to see the back of their head.
Types of Mirrors
1) Plane Mirror
- Object and Image are at equal distance from Plane Mirror.
- If object is real, then image will be virtual and vice versa.
- Size of image is equal to size of object.
- Uses: Looking Glass, Periscope, Kaleidoscope, etc.
2) Spherical Mirror
- Mirrors with curved reflecting surfaces that are part of a sphere.
- Types:
- Concave Mirror: Reflects light inward, used in telescopes, shaving mirrors, and headlights.
- Convex Mirror: Reflects light outward, used in vehicle rearview mirrors and security mirrors.
Dispersion of Light
- Dispersion is the phenomenon where white light separates into its constituent colors (spectrum) when it passes through a prism.
- When white light enters a prism, it slows down and bends due to refraction.
- The light spreads out into a spectrum of seven colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet (VIBGYOR).
Human Eye
Parts of the Human Eye
- Cornea: The transparent, curved outer layer that focuses incoming light.
- Pupil: The adjustable opening in the center of the eye that controls light entry.
- Iris: The colored part of the eye that surrounds the pupil and adjusts its size.
- Retina: The innermost layer with photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) that convert light into electrical signals.
- Aqueous and Vitreous Humors: Clear fluids in the front and back chambers that nourish the eye and maintain its shape.
- Optic Nerve: Transmits electrical signals from the retina to the brain.
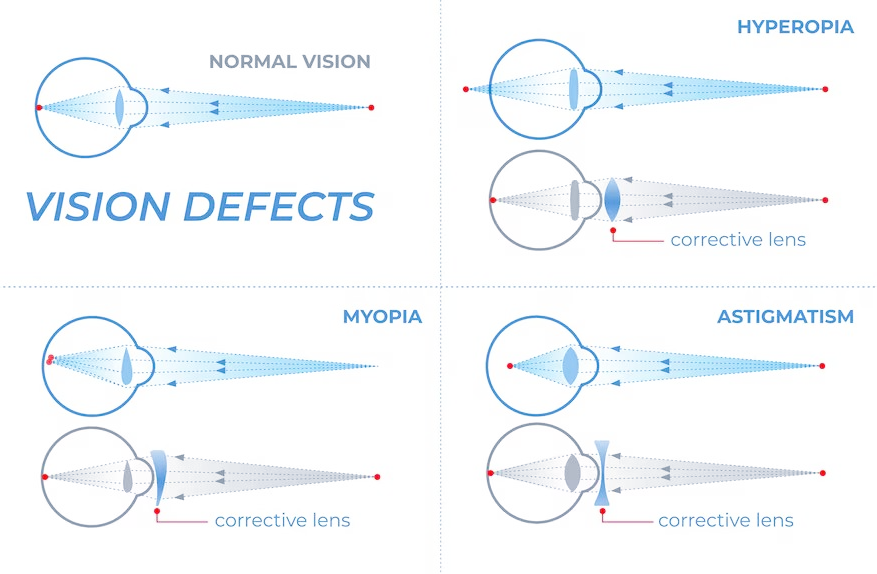
Defects of Vision
- Myopia (Nearsightedness): Difficulty seeing distant objects clearly due to an elongated eyeball or excessive curvature of the cornea.
Correction: Use concave lenses. - Hypermetropia (Farsightedness): Difficulty seeing close objects clearly due to a shortened eyeball or insufficient curvature of the cornea.
Correction: Use convex lenses. - Presbyopia: Age-related difficulty focusing on close objects due to loss of lens elasticity.
Correction: Use reading glasses or bifocals.
The World of the Blind
Louis Braille System: A tactile writing system using raised dots to enable visually impaired individuals to read and write by touch.
Subscribe to My Channel











No comments:
Post a Comment