Reproduction
➨Reproduction is the process by which living beings produce young ones of their own kind.
➥ It helps in maintaining the species.
➥ It helps in the continuity of life.
➥ It helps in maintaining of population size.
- Asexual Reproduction:
➥The production of a new organism from a single parent without the involvement of sex cells (or gametes) is called asexual reproduction - Sexual Reproduction:
➥The production of a new organism from two parents by making use of their Sex cells (or gametes) is called Sexual reproduction.
Ques. - Differentiate between Asexual Reproduction and Sexual Reproduction.

Asexual Reproduction
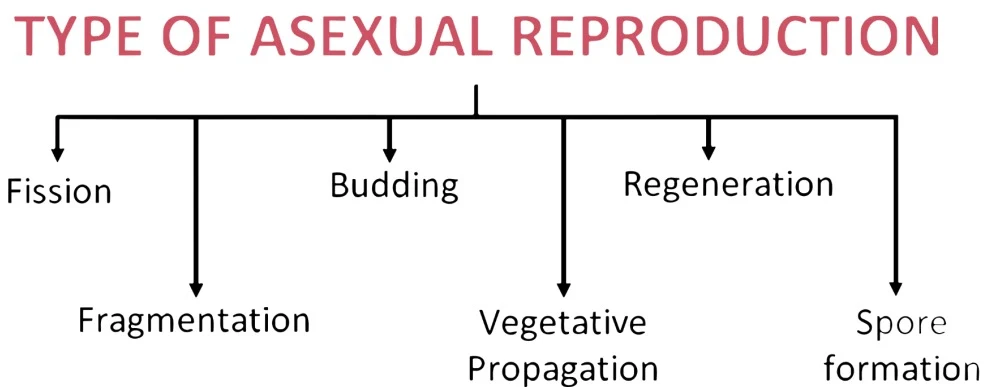
Types of Asexual Reproduction:
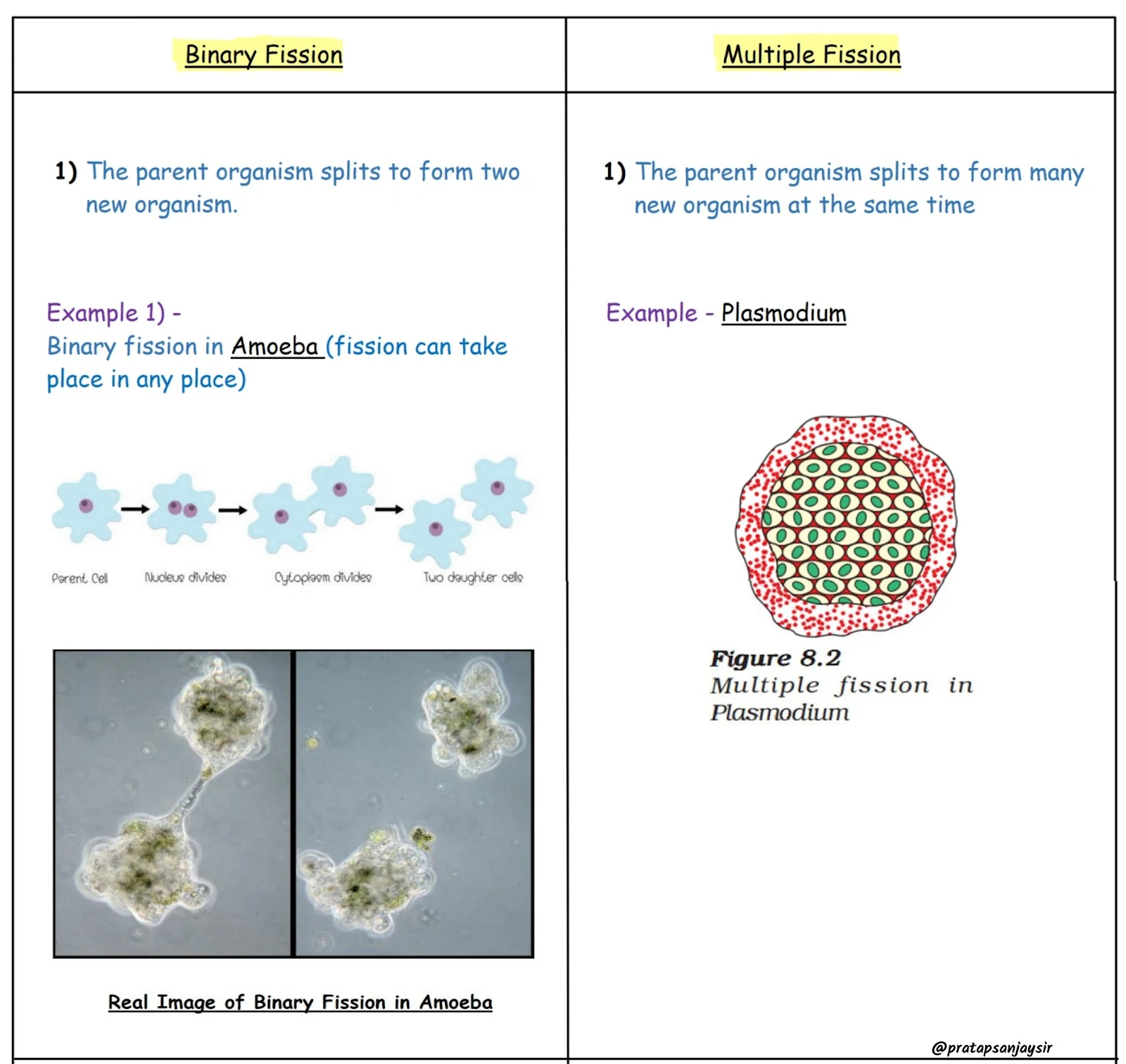
1. Binary Fission: A single organism divides into two equal parts, each developing into a new organism.
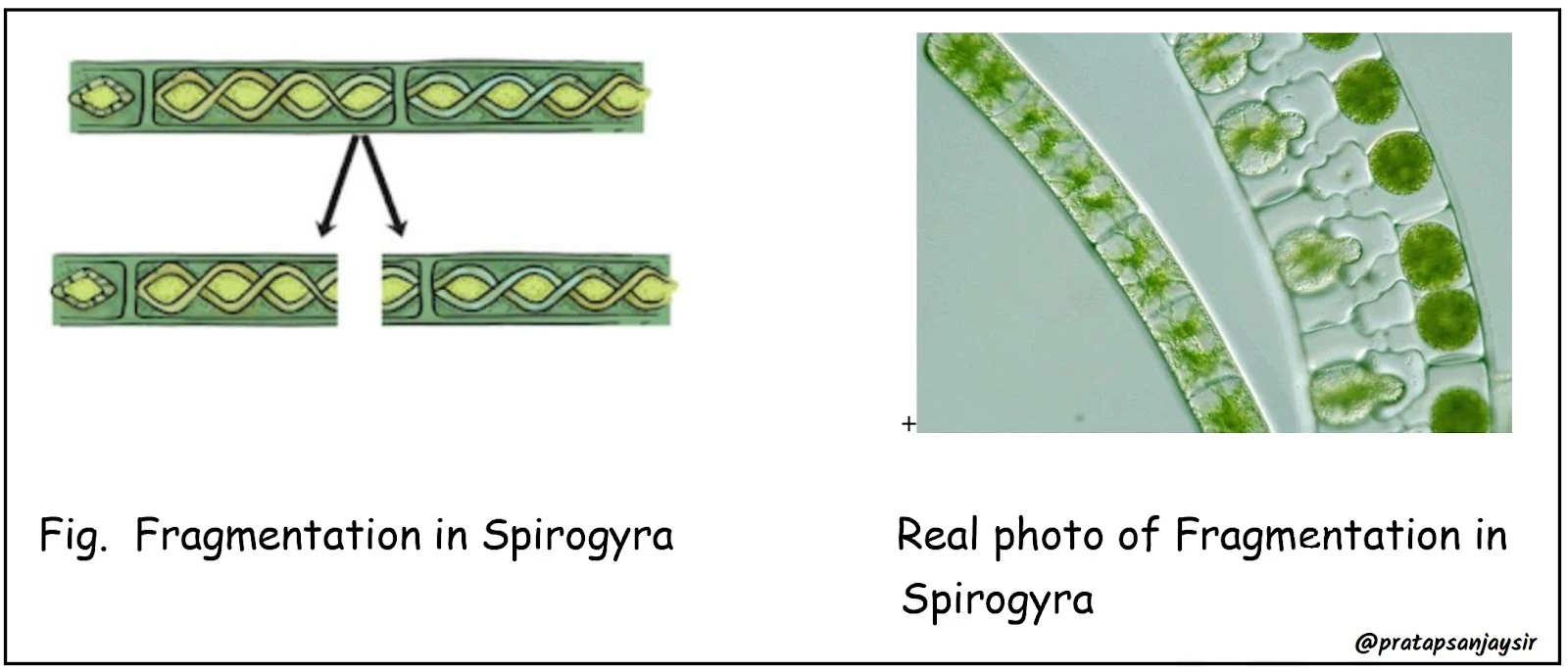
2. Fragmentation: The body of the parent breaks into fragments, each of which grows into a new organism.
3. Regeneration: The process of getting back a full organism from its body parts is called Regeneration.eg - Hydra and Planaria.

4. Budding: A new organism grows from a small bud on the parent and eventually detaches to live independently.

5. Spore Formation: Spores are produced by the parent, which can grow into a new organism under favorable conditions.

6. Vegetative Propagation: New plants grow from the vegetative parts of the parent plant, such as roots, stems, or leaves.

Sexual Reproduction
⟹ Sexual Reproduction involves the fusion of gametes or sex cells resulting in the formation of zygote.
⟹ Due to the fusion of gametes, the chances of variations are very high during sexual reproduction.

Sexual reproduction in Flowering Palnts
➥The Sex Organs (or reproductive organs) of a plant are in its flowers.

(1). Stamen: It is the male reproductive part of the flower. It is composed of two parts:
- Anther: Produces pollen grains that are yellow in color.
- Filament: Supports the anther.
(2). Pistil: It is the female reproductive part of the flower. It is composed of three parts:
- Ovary: The swollen bottom part.
- Style: The middle elongated part.
- Stigma: The terminal sticky part.
(3). Sepals: The green, leaf-like parts of the flower. Their function is to protect the flower in its initial stages.
(4). Petals: The colorful parts of a flower. Their function is to attract insects for pollination and protect the reproductive organs.
➯ Types of Flower:
Unisexual Flowers: Contains either stamens or pistils.
- eg: Papaya, Watermelon.
Bisexual Flowers: Contains both stamens and pistils.
- eg: Hibiscus, Mustard.
Sexual reproduction in Flowering Palnts
➥The age at which sex hormones and gametes begin to be produced, and when boys and girls become sexually mature, is called Puberty.
In males: After puberty, the testes start producing sperms and the male sex hormone called testosterone.
In females: After puberty, the ovaries start producing ova (or eggs) and the female sex hormone, estrogen.
➯Both males and females also start developing secondary sexual characteristics.
Secondary Sexual Characteristics in Males:
- Hair grows in armpits, pubic regions, chest, and face.
- The body becomes more muscular.
- The voice deepens.
- The chest and shoulders broaden.
Secondary Sexual Characteristics in Females:
- Hair grows in armpits and pubic regions.
- Mammary glands develop and enlarge.
- Hips broaden.
- The fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina enlarge.
Male Reproductive System

➥The male reproductive system consists of parts that perform two major functions:
- Produce sperms: Testes
- Deliver sperms to the site of fertilization: All the rest (Vas deferens, Seminal Vesicle, Prostate)
(1). Testes
➥ The testes are the primary reproductive organs in males.
➥ They are located outside the abdominal cavity in the scrotum because sperm formation requires a lower temperature than normal body temperature.
Functions of Testes:
- Formation of sperms.
- Secretion of testosterone.
(2). Vas Deferens
➥ The vas deferens delivers sperms from the testes to the urethra.
(3). Prostate and Seminal Vesicle
➥ The seminal vesicle and prostate gland add fluid secretions to the sperms, making their transport easier and providing nutrition.
(4). Urethra
➥ The urethra forms a common passage for both sperms and urine.
Female Reproductive System

1. Ovaries:
➥ The ovaries are the primary reproductive organs in females. They perform two major functions:
- Production of eggs (ova).
- Secretion of estrogen and progesterone.
➥One egg is produced every month by the ovaries.
2. Fallopian Tubes (Oviducts):
➥It is the primary reproductive organ in female.
➥It acts as the site of fertilization.
3. Uterus:
➥The oviducts unite into an elastic, bag-like structure known as the uterus.
➥ The uterus opens into the vagina through the cervix.
4. Vagina:
➥ The vagina receives sperms from the male partner and serves as a birth canal.
5. Cervix:
➥ The uterus is connected to the vagina through a narrow opening called the cervix.
Subscribe to My Channel



No comments:
Post a Comment